How Hydroponic Systems Can Revolutionize Urban Agriculture
In recent years, urban agriculture has played an increasingly central role in sustainability strategies and food logistics in cities. With the rising urban population and the growing need to reduce the environmental impact of the agricultural sector, hydroponic systems are emerging as an innovative and promising solution.
What Are Hydroponic Systems?
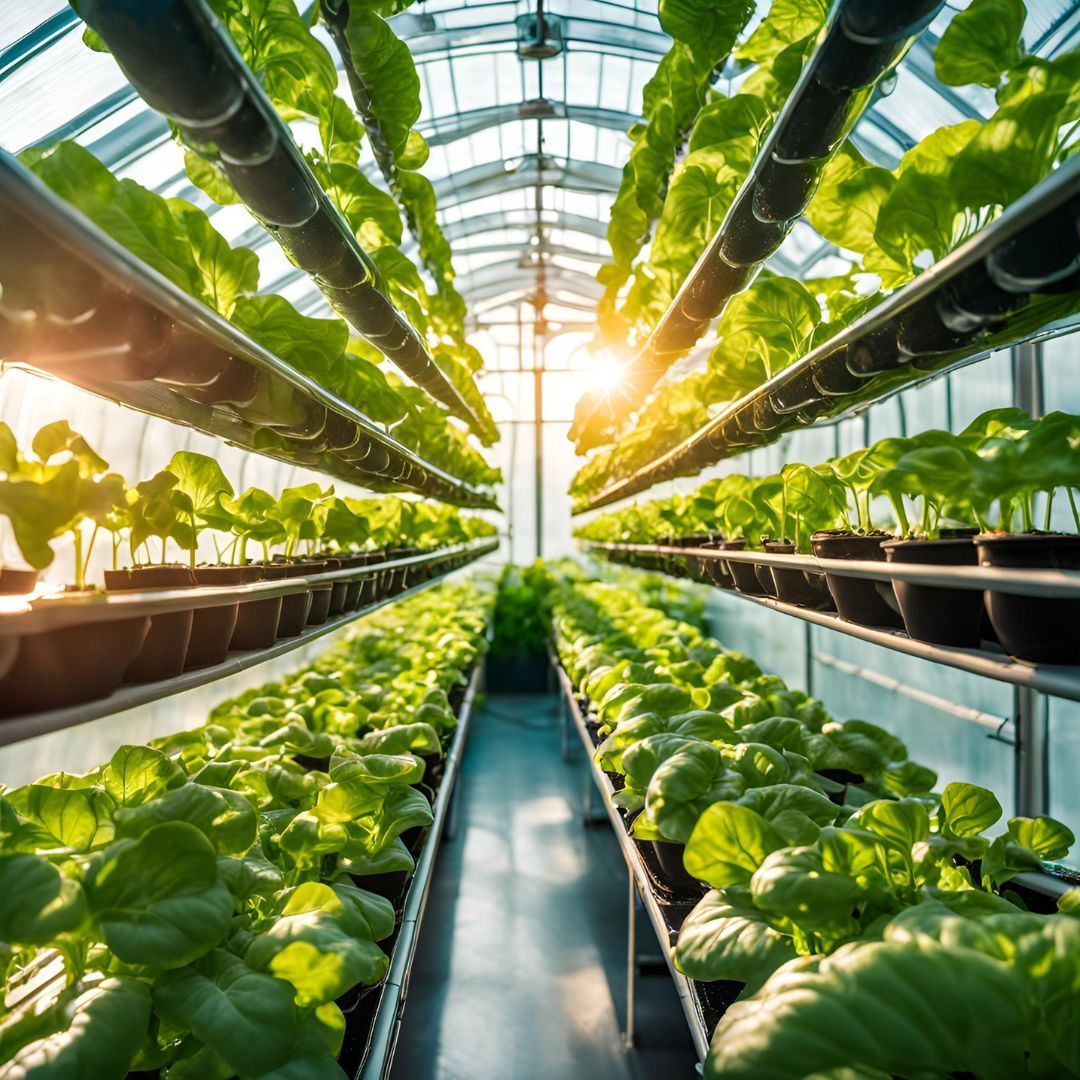
Hydroponics is a cultivation technique that does not use soil but relies on nutrient-rich aqueous solutions to nourish plants. This method allows for more efficient resource management and significantly reduces water consumption compared to traditional agriculture.
The Advantages of Hydroponics in Urban Agriculture
Space Optimization:
Hydroponic systems can be implemented in limited urban spaces such as rooftops, balconies, or abandoned buildings, transforming them into productive areas.
Reduced Water Consumption:
Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional methods, thanks to the recycling of nutrient solutions.
Elimination of Pesticides:
Since it is a controlled environment, the need for chemical pesticides is reduced, contributing to more sustainable production.
Local Production and Reduced Logistics Impact:
Growing food directly in cities shortens the supply chain, reducing CO2 emissions from transportation and ensuring fresher products.
Faster Growth and Higher Productivity:
Thanks to precise control of nutrients and environmental conditions, plants grow faster and yield more than in traditional agriculture.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite numerous advantages, large-scale adoption of urban hydroponics presents some challenges. The initial cost of infrastructure and the need for technical expertise can be obstacles. However, with technological advancements and government policies focused on sustainability, hydroponics could become a key component of future cities.
In conclusion, hydroponic systems offer a concrete opportunity to revolutionize urban agriculture, making it more efficient, sustainable, and resilient. Investing in these technologies means promoting a future where cities are not just centers of consumption but also hubs of responsible food production.