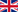
Agenda 2030: A Global Plan for a Sustainable Future
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development is an ambitious program adopted in September 2015 by the 193 member states of the United Nations. This global plan represents a collective commitment to address the most urgent challenges of the contemporary world, aiming to transform our society into a more just, prosperous, and sustainable place by 2030.
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
At the heart of the 2030 Agenda are the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a set of integrated targets that encompass three fundamental dimensions of sustainable development: economic, social, and environmental. These goals tackle a wide range of global issues, including poverty, hunger, gender inequality, climate change, urban sustainability, biodiversity protection, access to education, and universal healthcare.Each goal is further divided into specific targets, totaling 169, which set the standards and milestones for monitoring progress at both global and national levels. This integrated and interconnected approach recognizes that sustainable development challenges are interdependent and require holistic and cooperative solutions.
A Universal Commitment
The 2030 Agenda is not just about governments; it is a universal commitment that also involves the private sector, civil society organizations, local communities, and every individual citizen. Its implementation requires collaboration and participation from all sectors of society. Governments are called upon to create policies and establish legislative frameworks that promote sustainable development, while businesses must integrate sustainability into their operations and strategies. At the same time, communities and individuals are encouraged to adopt more sustainable practices and contribute to social change.
The Challenge of Climate Change
One of the most urgent goals of the 2030 Agenda is the fight against climate change, recognized as an existential threat to our planet. Goal 13 ("Climate Action") focuses on taking urgent measures to combat climate change and its impacts. This includes promoting renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable management of natural resources, and the adoption of resilient agricultural practices.
Education, Equality, and Justice
Other crucial goals include quality education (Goal 4), which aims to ensure inclusive and quality education for all, and gender equality (Goal 5), which seeks to eliminate all forms of discrimination and violence against women and girls. Lastly, Goal 16 aims to promote peaceful and inclusive societies, ensuring access to justice for all and building accountable and transparent institutions.
Progress and Challenges
Nearly a decade since the adoption of the 2030 Agenda, significant progress has been made in some areas, but many challenges remain unresolved. The COVID-19 pandemic has slowed progress in many sectors, exacerbating existing inequalities and making the need for concerted and urgent action even more apparent.However, the 2030 Agenda continues to represent a beacon of hope and a guiding framework for a better future. Its success depends on our ability to work together at the global, national, and local levels, taking bold and innovative measures to ensure that no one is left behind.
The 2030 Agenda is more than just a plan; it is a call to action to address the most critical issues of our time and build a sustainable future for present and future generations. As we approach 2030, it is essential that all stakeholders intensify their efforts to realize this shared vision of peace, prosperity, and respect for our planet.